ETH researchers compute turbulence with artificial intelligence
For the first time, researchers at ETH Zurich have successfully automated the modelling of turbulence. Their project relies on fusing reinforcement learning algorithms with turbulent flow simulations on the CSCS supercomputer "Piz Daint".
The modelling and simulation of turbulent flows is crucial for designing cars and heart valves, predicting the weather, and even retracing the birth of a galaxy. The Greek mathematician, physicist and engineer Archimedes occupied himself with fluid mechanics some 2,000 years ago, and to this day, the complexity of fluid flows is still not fully understood. The physicist Richard Feynman counted turbulence among the most important unsolved problems in classical physics, and it remains an active topic for engineers, scientists and mathematicians alike.
Engineers have to consider the effects of turbulent flows when building an aircraft or a prosthetic heart valve. Meteorologists need to account for them when they forecast the weather, as do astrophysicists when simulating galaxies. Consequently, researchers from these communities have been modelling turbulence and performing flow simulations for more than 60 years.
Turbulent flows are characterized by flow structures spanning a broad range of spatial and temporal scale. There are two major approaches for simulating these complex flow structures: One is direct numerical simulation (DNS), and the other is large eddy simulation (LES).
Flow simulations test the limits of supercomputers
DNS solves the Navier-Stokes equations, which are central to the description of flows, with a resolution of billions and sometimes trillions of grid points. DNS is the most accurate way to calculate flow behaviour, but unfortunately it is not practical for most real-world applications. In order to capture the details of these turbulent flows, they require far more grid points than can be handled by any computer in the foreseeable future.
As a result, researchers use models in their simulations so that they do not have to calculate every detail to maintain accuracy. In the LES approach, the large flow structures are resolved, and so-called turbulence closure models account for the finer flow scales and their interactions with the large scales. However, the correct choice of closure model is crucial for the accuracy of the results.
Rather art than science
“Modelling of turbulence closure models has largely followed an empirical process for the past 60 years and remains more of an art than a science”, says Petros Koumoutsakos, professor at the Laboratory for Computational Science and Engineering at ETH Zurich. Koumoutsakos, his PhD student Guido Novati, and former master’s student (now PhD candidate at the University of Zurich) Hugues Lascombes de Laroussilhe have proposed a new strategy to automate the process: use artificial intelligence (AI) to learn the best turbulent closure models from the DNS and apply them to the LES. They published their results recently in "Nature Machine Intelligence".
Specifically, the researchers developed new reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms and combined them with physical insight to model turbulence. "Twenty-five years ago, we pioneered the interfacing of AI and turbulent flows," says Koumoutsakos. But back then, computers were not powerful enough to test many of the ideas. "More recently, we also realised that the popular neural networks are not suitable for solving such problems, because the model actively influences the flow it aims to complement," says the ETH professor. The researchers thus had to resort to a different learning approach in which the algorithm learns to react to patterns in the turbulent flow field.
Automated modelling
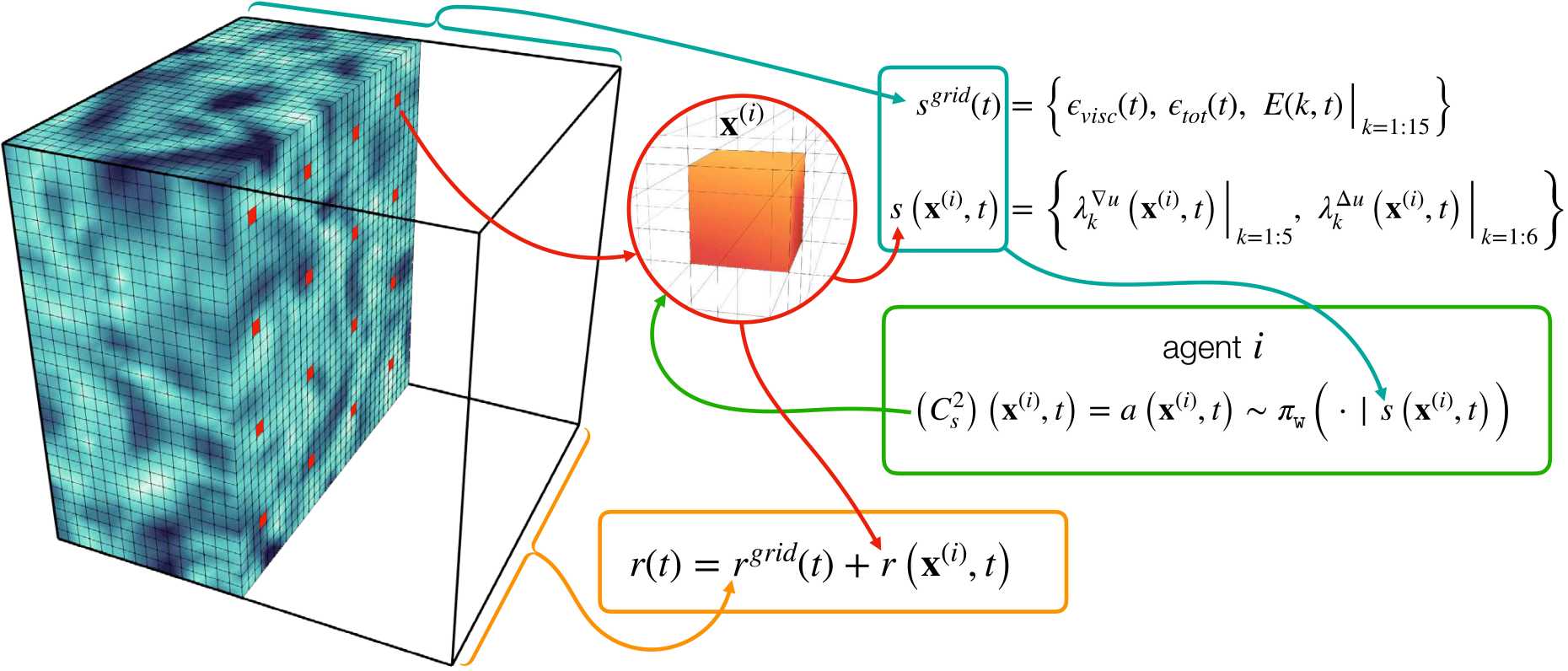
The idea behind Novati’s and Koumoutsako's novel RL algorithm is to use the grid points that resolve the flow field as AI agents. The agents learn turbulence closure models by observing thousands of flow simulations. “In order to perform such large scale simulations, it was essential to have access to the CSCS supercomputer "Piz Daint", stresses Koumoutsakos. After training, the agents are free to act in the simulation of flows in which they have not been trained before.
The turbulence model is learned by ‘playing’ with the flow. “The machine ‘wins’ when it succeeds to match LES with DNS results, much like machines learning to play a game of chess or GO" says Koumoutsakos. “During the LES, the AI performs the actions of the unresolved scales by only observing the dynamics of the resolved large scales.” According to the researchers the new method not only outperforms well-established modelling approaches, but can also be generalised across grid sizes and flow conditions.
The critical part of the method is a novel algorithm developed by Novati that identifies which of the previous simulations are relevant for each flow state. The so-called "Remember and Forget Experience Replay" algorithm has been shown to outperform the vast majority of existing RL algorithms on multiple benchmark problems beyond fluid mechanics, according to the researchers. The team believes that their newly developed method will not only be of importance in the construction of cars and in weather forecasting. "For most challenging problems in science and technology, we can only solve the 'big scales' and model the 'fine' ones," says Koumoutsakos. "The newly developed methodology offers a new and powerful way to automate multiscale modelling and advance science through a judicious use of AI.”
Reference
Novati G, Lascombes de Laroussilhe H & Koumoutsakos P: Automating turbulence modelling by multi-agent reinforcement learning, Nature Machine Intelligence, January 4 2021, DOI: external page 10.1038/s42256-020-00272-0
Related Articles
- chevron_right The Indian who set out to reveal the secret of turbulent fluid flows (ETH-News 23.07.2018)
- external page call_made A research career shaped by supercomputing (CSCS-News 07.03.2018)
- external page call_made ETH research among the best supercomputer applications in 2015 (CSCS-News 09.11.2015)
Comments
Additional comments are available for the German version of this article. Show all comments
Why we can't use experimental results using piv data to train the AI model and apply the trained model in CFD code
We can use experimental results and we advocate so in the paper ! Here we used accurate flow simulations for training to avoid uncertainties associated with experiments. But again such uncertainties can be accounted for in the turbulence models through AI.
This sounds like another way to do data assimilation. If there are sufficient obs data for large scales, then let AI decide LES parameters. Is this interpretation plausible? What is the advantage over existing DA methods?
The RL algorithm uses data and accurate simulations for training. After training the RL does not require data like DA does. RL builds models based on patterns in the coarse grain features of the flow and its experiences from training. More details on comparing RL and other methods are in the referenced paper.