Two projects launched to connect error-corrected qubits
ETH Zurich is participating in two quantum computing projects that are being financed by IARPA, the US research funding agency, with up to 40 million dollars. Both projects aim to connect two error-corrected qubits with one another and thus lay the foundation for future quantum computers.
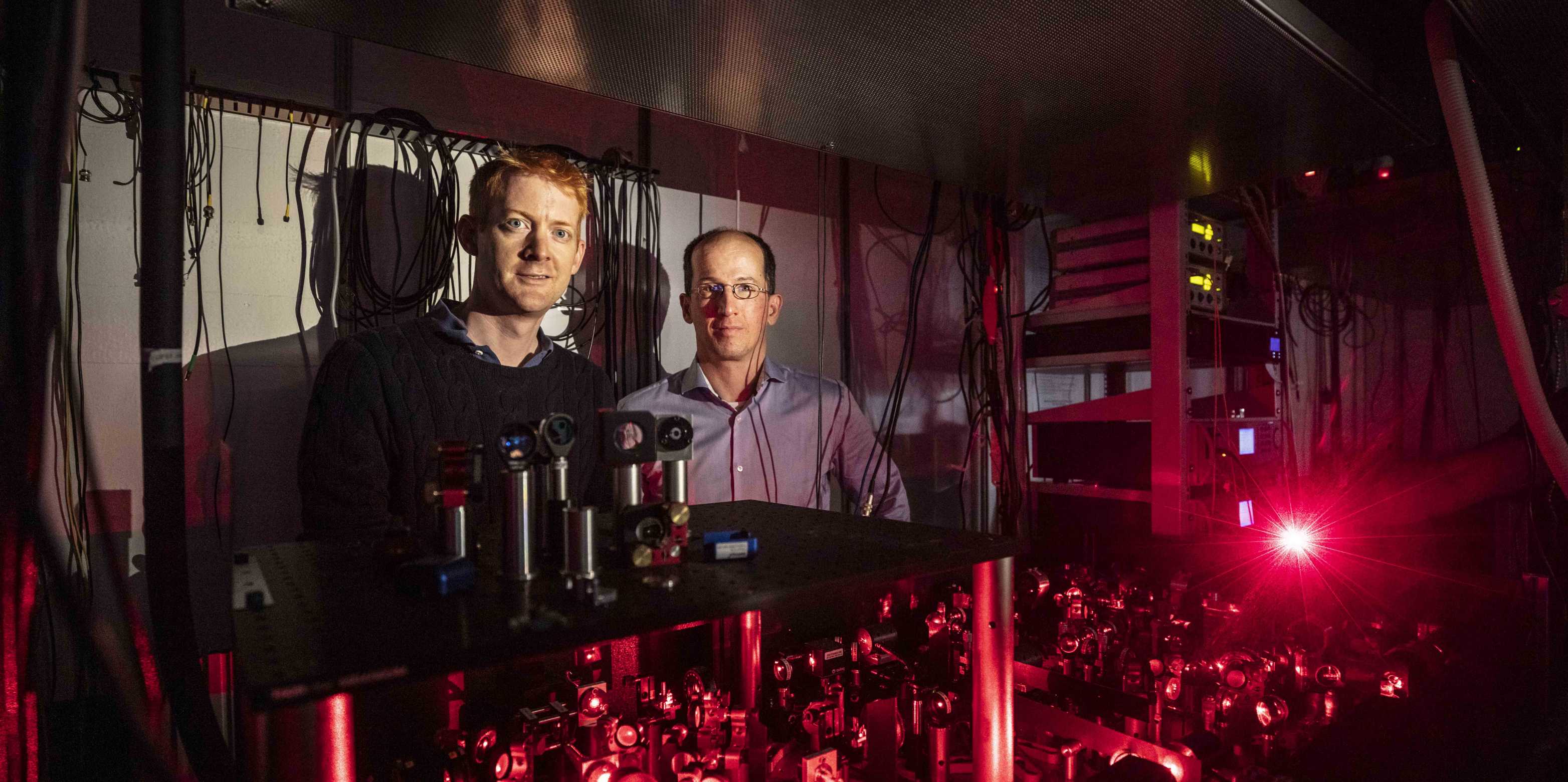
Jonathan Home and Andreas Wallraff are attempting to entangle two logical qubits and transferring the quantum state of one logical qubit to the other. (Photograph: KellenbergerKaminski Photographie / ETH-Rat)
Comments
No comments yet