ETH News
All stories by Rahel Künzler
A wooden dome made solely from waste
Globe magazine

Catherine De Wolf firmly believes that digitalisation can help shift the construction industry towards a more circular economy. The assistant professor and her research group recently completed a hands-on project to illustrate how this could work.
How human and artificial intelligence can augment one another
News

Mennatallah El-Assady develops explainable AI programs that explain their own workings – and let users provide input. This can help analysts take a deep dive into political debate.
ETH graduates reinvent the user manual
News

No sooner had David Shapira and Kordian Caplazi finished their studies than they set about creating a start-up. Rimon develops virtual user manuals for industrial companies, enabling users to quickly and intuitively learn how to operate complex machines with the aid of AR glasses.
New drug candidates identified in bacteria
News
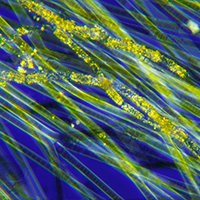
Bacteria show great promise as a source of active ingredients. Using computer-based genome analysis, researchers at ETH Zurich have now discovered a new class of natural products that might one day serve as antibiotics.
Exploring the architecture of tumours
News
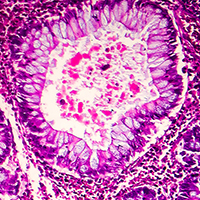
ETH researchers have used computer simulations to show that tissue structure in different types of cancer is decisive in determining how a tumour develops. This information could make it possible to treat patients in a more targeted manner in future.
Almost all chemicals burden the planet
News

For the first time, researchers at ETH Zurich have calculated in absolute figures the extent to which the production of chemicals is currently interfering with nature worldwide – and the results are staggering. In addition to greenhouse gas emissions, the new method also takes land use and freshwater consumption into account.
One step closer to lifelike avatars
News
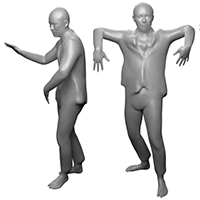
Soon, internet users will be able to meet each other in cyberspace as animated 3D avatars. Researchers at ETH Zurich have developed new algorithms for creating virtual humans much more easily.
Agents between good and evil
News
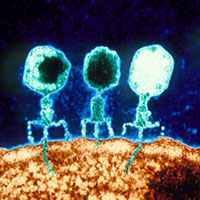
Viruses that infect bacteria could one day replace antibiotics because they precisely attack only specific pathogens. Researchers at ETH Zurich are now showing that this is not always the case. This new finding is important because bacterial viruses can transfer antibiotic resistance genes.
AI offers a faster way to predict antibiotic resistance
News

A study under co-leadership of the ETH Zurich has shown that computer algorithms can determine antimicrobial resistance of bacteria faster than previous methods. This could help treat serious infections more efficiently in the future.
Climate change is intensifying extremes also in the oceans
News

While much is known about extreme weather events on land, there has been little research into those that occur in the ocean. A study led by ETH Zurich uses models to show for the first time that marine heatwaves, and extremes with high acidity or low oxygen can also occur conjointly – with difficult to foresee consequences for marine life.
Rapid PCR tests at the touch of a button
News

ETH researchers Michele Gregorini and Philippe Bechtold have developed a PCR testing device that can easily be used outside the lab – and that takes less than 30 minutes to deliver results. Now the two young entrepreneurs are focusing their efforts on getting the device approved for medical use.
Finding inspiration in starfish larva
News
Researchers at ETH Zurich have developed a tiny robot that mimics the movement of a starfish larva. It is driven by sound waves and equipped with tiny hairs that direct the fluid around it, just like its natural model. In the future, such microswimmers could deliver drugs to diseased cells with pinpoint accuracy.
Examining the skin with a vacuum
News

Biomechanical engineer Bettina Müller has developed a device that can improve examinations of how scars heal. She hopes her device will help doctors to diagnose skin diseases. “Nimble” is set to go to market within two years.