ETH News
All stories by Daniel Meierhans
Knocking cloud security off its game
News

Public cloud services employ special security technologies. Computer scientists at ETH Zurich have now discovered a gap in the latest security mechanisms used by AMD and Intel chips. This affects major cloud providers.
Finding and blocking infection routes in hospitals
News

During the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals often became hubs of infection. Researchers from ETH Zurich, EPFL and the ISI Foundation are developing a wearable tracking system for healthcare facilities that can identify the risks of infections. Initial tests in Switzerland and Africa show its potential.
A sustainable fuel and chemical from the robotic lab
News

Artificial intelligence and automated laboratory infrastructure are massively accelerating the development of new chemical catalysts. With these tools, researchers at ETH Zurich are developing catalysts for efficiently and cost-effectively synthesising the energy source methanol from CO2.
New agent blocks stress response
News

If the body’s natural stress response gets knocked off balance, it can result in physical and mental health disorders. Researchers at ETH Zurich have developed an agent capable of selectively inhibiting this response.
Artificial intelligence finds ways to develop new drugs
News

A new AI model developed by chemists at ETH Zurich can not only predict where a pharmaceutically active molecule can be chemically modified, but also how best to do it. This makes it possible to identify new pharmaceutical ingredients more quickly and improve existing ones in a targeted manner.
Measuring earthquakes and tsunamis with fibre-optic networks
News

Geophysicists at ETH Zurich have shown that every single wave of a magnitude 3.9 earthquake registers in the noise suppression system of fibre-optic networks. This method can be used to set up close-meshed earthquake and tsunami early warning systems at low cost.
Orexin influences pupil size
News
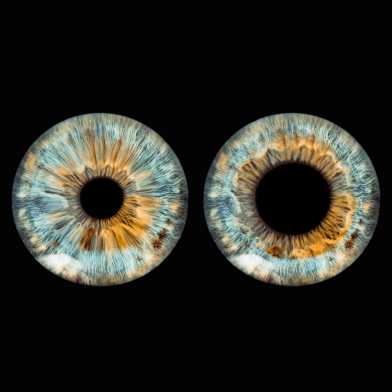
The way the brain regulates pupil size is different from previously thought: fundamentally responsible is the neurotransmitter orexin, as researchers at ETH Zurich have now shown. This discovery could well alter our understanding of consciousness and illnesses such as narcolepsy and Alzheimer’s.
Lasers enable internet backbone via satellite
News

Optical data communications lasers can transmit several tens of terabits per second, despite a huge amount of disruptive air turbulence. ETH Zurich scientists and their European partners demonstrated this capacity with lasers between the mountain peak, Jungfraujoch, and the city of Bern in Switzerland. This will soon eliminate the necessity of expensive deep-sea cables.
Accurate rapid tests made from smart graphene paper
- News
- Homepage
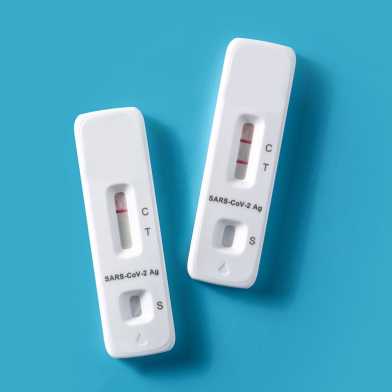
A team led by ETH Zurich chemical engineers Chih-Jen Shih and Andrew deMello have developed a rapid test system made of smart graphene paper. It only costs a few cents per test strip, is easy to use but is as accurate as lab measurements. The approach will impact more than just disease monitoring.
Breathing life into video pixels
News

Autonomous virtual humans that move and behave naturally are Siyu Tang’s vision. One area from which the computer scientist draws inspiration are our behavioural patterns. Collaboration with architects and surgeons provides further input – and it also reveals the enormous potential of virtual people.
New reaction facilitates drug discovery
News
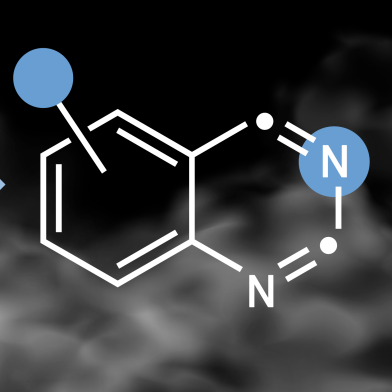
Chemists at ETH Zurich have found a facile method that allows a commonly used building block to be directly converted into other types of important compounds. This expands the possibilities of chemical synthesis and facilitates the search for new pharmaceutically active ingredients.
Using statistical methods to predict the course of disease
News

Data contains much more than just the information on the surface. With statistics, deeper cause-and-effect relationships can be brought to light. This is what Alexander Marx is researching as a Fellow at the ETH AI Center using artificial intelligence. One of his goals is to be able to make predictions regarding diabetes in children.
Fibres make chaotic turbulence more predictable
News

The chaotic behaviour of vortices is one of the things that makes weather forecasting so difficult. Researchers at ETH Zurich have now developed a novel experimental method that enables more accurate analyses of the movement of turbulence in fluids.
Harnessing AI to discover new drugs inspired by nature
News

Artificial intelligence (AI) is able to recognise the biological activity of natural products in a targeted manner, as researchers at ETH Zurich have demonstrated. Moreover, AI helps to find molecules that have the same effect as a natural substance but are easier to manufacture. This opens up huge possibilities for drug discovery, which also have potential to rewrite the rulebook for pharmaceutical research.
450 logic errors found in popular databases
News

Database systems are under pressure to become more and more powerful. But reliability seems to be suffering as a result. Now, ETH computer scientists have developed a tool to automatically detect logic errors in database systems using three different methods. They found and reported over 450 unique, previously unknown bugs.
Our actual attention is now measurable
News

We want to make sure our phones no longer disturb us at the wrong moment. To achieve this, we first have to better understand where our attention lies when using smartphones. Computer scientists at ETH have now developed a system that records eye contact with the display in everyday situations for the first time. Sociologists and medical experts could also benefit from this.
A robot that controls highly flexible tools
News
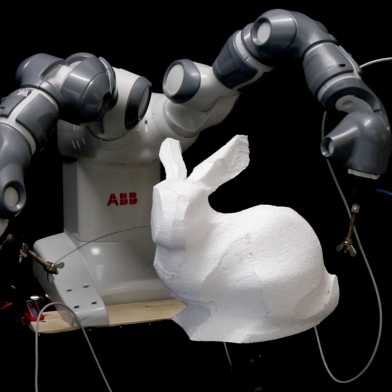
How do you calculate the coordinated movements of two robot arms so they can accurately guide a highly flexible tool? ETH researchers have integrated all aspects of the optimisation calculations into an algorithm. The hot-wire cutter will be used, among other things, to develop building blocks for a mortar-free structure.